Business leaders must avoid confusing IT Security, Information Security and Cyber Security. They are related, they share disciplines, principles, and in some cases, tactics, but they are not the same things. The approach and strategy of Cyber Security is very different than the approach and strategy of IT Security or Information Security. Confusion of these elements will prevent Executives from applying resources and capital in the most effective ways.
Each security context deals with risk introduced by different components of technology, process, and people. In many cases, when applying IT or IS practices to a Cyber Security effort, the risks that get reported often do not get mitigated because the over-arching strategy is flawed. The findings are reported in the wrong context.
IT Security has traditionally focused on hardware and software security solutions. This approach requires healthy investments in hardware and software that must be managed, groomed and updated. This strategy usually excludes vital Information Security practices like valuation, data mapping, risk management and governance functions such as information or data classification.
In the Cyber Security context, the manager needs to develop a focus on public facing telecommunication networks and the handling of mobile equipment and media that store sensitive information. Any public access to information electronically needs to be risk assessed and risk treated.
In the Information Security context, the manager should focus on internal access mechanisms and data flows, internal controls, audit trails, and perimeter controls. Without all of these critical building blocks in place, the design, implementation and day-to-day operations will be incomplete. The Enterprise Information Security Program will be vulnerable.
- IT Security focuses on securing technology through the use of primarily technological controls. This security is intended to ensure that Information Technology works as it should, and applies policy and practice to configuration, change and other management functions.
- Information Security focuses on securing access to proprietary information in any form, from the network core out to the perimeter, including controlling printed information and internal users. InfoSec seeks to safeguard both physical and digital data and resources from unauthorized use, access, disruption, inspection, modification, destruction or recording. This security is to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. In case a business is beginning to generate a security program, Information Security is where they should start since it is the foundation of the data security practice.
- Cyber Security focuses on defending against unauthorized access to digital information only, from external networks to the perimeter. Cyber Security safeguards computers, data, and networks of an organization, defending against unauthorized digital attack, access, or damage by implementing processes, practices, and technologies. This security is to prevent the data, network, and reputation of the company against electronic attack from external parties.
All of these security disciplines will overlap, as they are attempting to apply the same or similar principles within their own contexts. Here is a handy diagram.
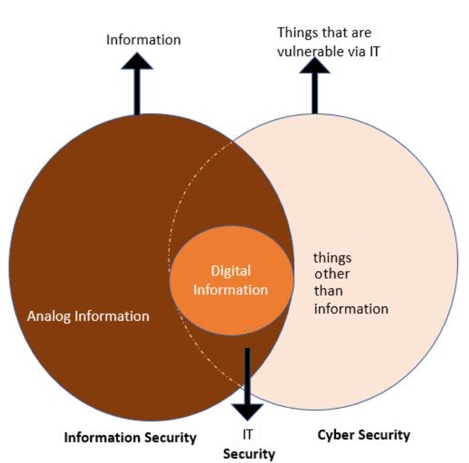
A holistic security strategy will contain all 3 security contexts, separated tactically, but operating harmoniously through interwoven processes. Outputs and results from one context should feed inputs into the underlying processes of the other two.